The easiest way to represent and understand the interaction of subatomic particles is by using Feynman Diagrams.
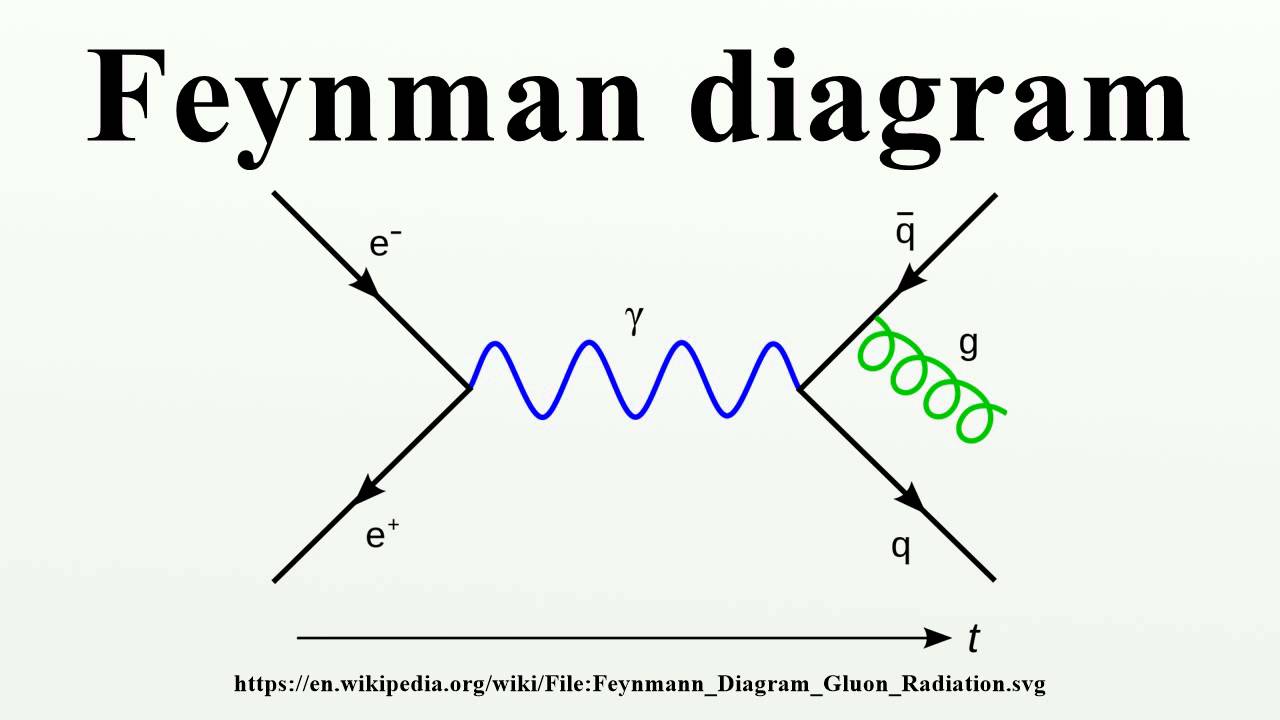
In theoretical physics, this method is used as a pictorial representation of the mathematical expressions of the behaviour of subatomic particles. This method was given by one of the famous scientist and lecturer Richard Phillips Feynman.

These diagrams are used to calculate the most difficult equations using diagrams.
For example collision of two electrons: When two electrons collide they interact with each other and scatter apart. The interaction happens as follows:
When two electrons are brought together they repel each other and move apart. This repulsion takes place due to the exchange of the gauge bosons. Gauge boson exchange is otherwise known as the exchange of particle or information. These are virtual particles.
Here photons are the exchange particle involved.
The photon released from one particle hits another electron and changes its path.
Thus represented by the given diagram below:

Rules to draw Feynman diagram are:
1. Time is always pointed upwards.
2. Space is on the x-axis moving forward towards the right.
3. Always start the incoming subatomic from down
4. The interaction or the process is represented in between
5. And the outgoing subatomic particles are represented at the top
The below figure illustrates the representation used to represent different particles involved:
The diagrams can be more complicated for the above-given example if we consider the emission of photons before or after the process or else emission and reabsorption of photons before or after the process.
There can be a particle and antiparticle formation during the exchange of photons.

These diagrams are used to find more accurate equations for the phenomena occurred.
Each time a photon interacts with a charged particle the chance of the phenomena to happen is less likely. Single emission of photon drops to 1% of 1% i.e, 0.01%.
For more detailed understanding from the basic level of particles involved in the standard model we take the example of :

With the emission of a W boson, the quarks change their behaviour and form a different subatomic particle.
The interaction of particles is a very interesting and vast topic.
For further understanding visit:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1602.04182.pdf
https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feynman_diagram
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DiracbPic-5a3d1d78482c5200368c13e8.jpg)





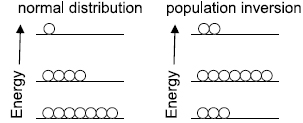
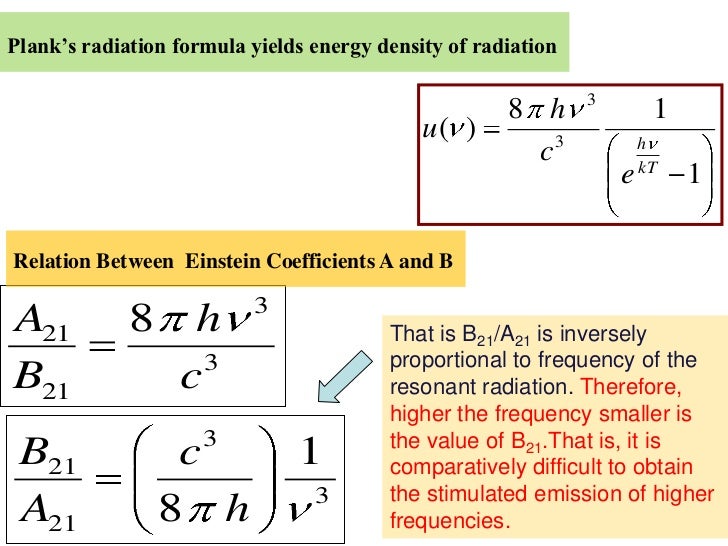
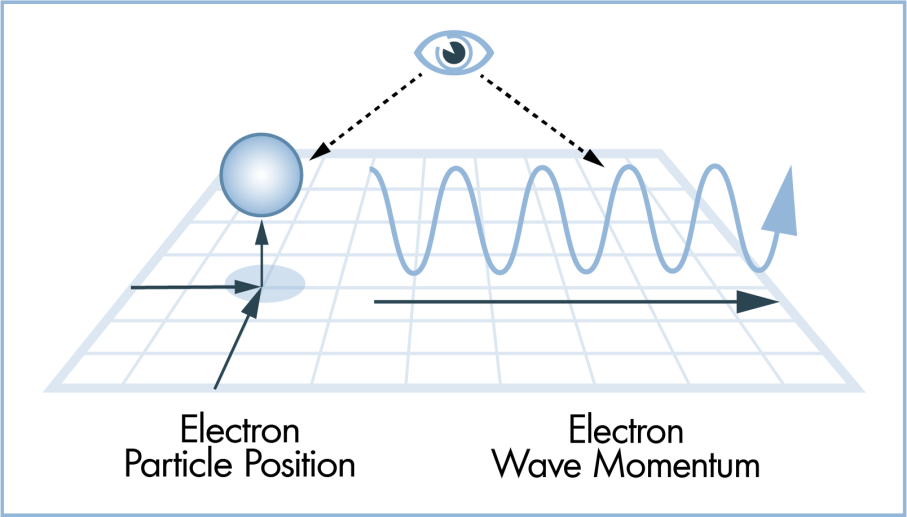





 Here is the data recorded from LIGO Livingston and LIGO Hanford.
Here is the data recorded from LIGO Livingston and LIGO Hanford.


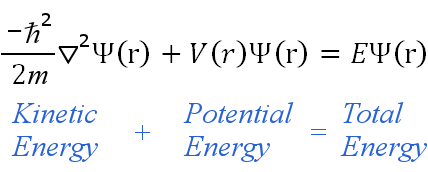
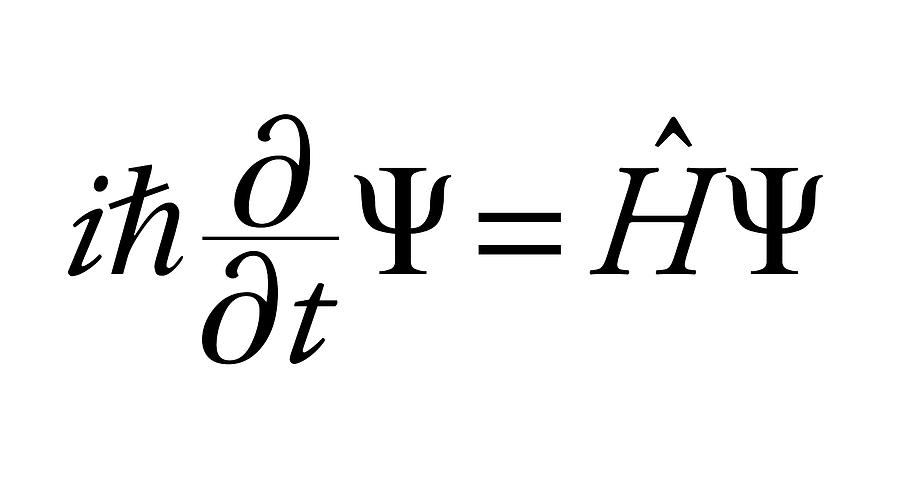
 = Wave function (psi) E= Energies of the electron is allowed to have
= Wave function (psi) E= Energies of the electron is allowed to have 



